Thermocouple
Thermocouple is a widely used temperature sensor and is also used to convert thermal potential difference into potential difference. It is cheap, easy to replace, has a standard interface, and has a large temperature range. Our company has a CTP calibration center that is certified by the TAF National Certification Foundation (ISO/IEC 17025:2005) and can provide actual measurement standards for accuracy.
Common Temperature Probes style
Thermocouple material
| Type | Material | Range | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | +70%Platinum +30%Rhodium |
0~1700°C | The mechanical strength and melting point are higher than RS. It is recommended to be used in oxidizing media or inert gas; it cannot be used in reducing media or metal vapors. The electromotive force is small and easily affected. Pay attention to contamination during use to avoid affecting accuracy. It is suitable for high temperature domain , but has poor accuracy in low temperature domain. |
| -94%Platinum +6%Rhodium |
|||
| R | +87%Platinum +13%Rhodium |
0~1450°C | The accuracy is similar to the S type but the mechanical strength is higher. It is recommended to be used in oxidizing media or inert gas; it cannot be used in reducing media or metal vapors. The electromotive force is small and easily affected. Pay attention to contamination during use to avoid affecting the accuracy. Suitable for high temperature areas. |
| -Platinum | |||
| S | +90%Platinum +10%Rhodium |
0~1450°C | Prior to the introduction of the 1990 International Temperature Scale (ITS-90), precision type S thermocouples were used as standard thermocouples in the range 630°C to 1064°C, based on the melting points of antimony, silver and gold. It is similar to type R in use. (Starting from ITS-90, platinum resistance thermometer is used as the standard thermometer) |
| -Platinum | |||
| K | +Nickel-Chromium | -200~1250°C | Recommended for use in oxidizing media or inert gas. After several improvements, it has a wide temperature range and is reliable, making it the most widely used thermocouple. |
| -Nickel-Aluminum | |||
| N | +Nickel +14.2%Chromium +1.4%Silicon |
-270~1300°C | It is an improved version of K type and is more stable than K type at high temperatures above 600°C. |
| -Nickel +Silicon4.4%+ Magnesium0.1% |
|||
| E | +Nickel-Chromium | -200~900°C | It is recommended to be used in oxidizing media or inert gas. The electromotive force generated by the temperature difference is large and easy to measure , so it is widely used in power plants. |
| -Copper-Nickel | |||
| J | +Iron | 0~750°C | Because the pure iron of the positive electrode is easily oxidized and rusted in an oxidizing environment with water vapor, it is recommended to be used in reducing media and inert gas. Not recommended for use in low temperature environments. |
| -Copper-Nickel | |||
| T | +Copper | -200~350°C | Recommended for use in mild oxidizing media and reducing media. Performs well in humid environments; mostly used in low temperature areas and refrigeration equipment. |
| -Copper-Nickel |
Thermocouple temperature resistant
| Wire diameter | JIS C 1602 | ANSI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JIC | ANSI | Maximum operating temperature for general use (°C) | Maximum operating temperature after heating (°C) | Maximum operating temperature (°C) | |
| B | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1500 | 1700 | 1700 |
| R | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1400 | 1600 | 1480 |
| S | 0.5 | 0.5 | |||
| K | 3.2 | 3.2 | 1000 | 1200 | 1260 |
| 2.3 | 900 | 1100 | |||
| 1.6 | 1.6 | 850 | 1050 | 1090 | |
| 1 | 750 | 950 | |||
| 0.8 | 980 | ||||
| 0.65 | 650 | 850 | |||
| 0.5 | 870 | ||||
| 0.32 | 870 | ||||
| J | 3.2 | 3.2 | 600 | 750 | 870 |
| 2.3 | 550 | 750 | |||
| 1.6 | 1.6 | 500 | 650 | 650 | |
| 1 | 450 | 550 | |||
| 0.8 | 540 | ||||
| 0.65 | 400 | 500 | |||
| 0.5 | 430 | ||||
| 0.32 | 430 | ||||
| E | 3.2 | 3.2 | 700 | 800 | 870 |
| 2.3 | 600 | 750 | |||
| 1.6 | 1.6 | 550 | 650 | 650 | |
| 1 | 500 | 550 | |||
| 0.8 | 540 | ||||
| 0.65 | 450 | 550 | |||
| 0.5 | 430 | ||||
| 0.32 | 430 | ||||
| T | 1.6 | 1.6 | 300 | 350 | 370 |
| 1 | 250 | 300 | |||
| 0.8 | 260 | ||||
| 0.65 | 200 | 250 | |||
| 0.5 | 200 | ||||
| 0.32 | 0.32 | 200 | 250 | 200 | |
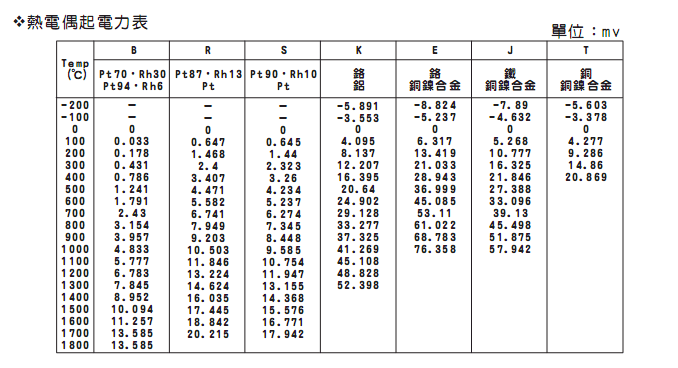
Thermocouple power meter
Thermocouple Accuracy
1.ASTM E230-1998, E988-1996
| Type | Temperature range | Allowable error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Special | ||
| B | Above 870°C; below 1700°C | 0.5% | - |
| R·S | Above 0°C; less than 1450°C | ±1.5°C or ±0.25% of measured temperature | ±0.6°C or ±0.10% of measured temperature |
| K | -200°C or above; less than 0°C | ±2.2°C or ±2.00% of measured temperature | - |
| Above 0°C; less than 1250°C | ±2.2°C or ±0.75% of measured temperature | ±1.1°C or ±0.40% of measured temperature | |
| N | -270°C or above; less than 0°C | ±2.2°C or ±2.00% of measured temperature | - |
| Above 0°C; below 1300°C | ±2.2°C or ±0.75% of measured temperature | ±1.1°C or ±0.40% of measured temperature | |
| E | -200°C or above; less than 0°C | ±1.7°C or ±1.00% of measured temperature | - |
| Above 0°C; below 900°C | ±1.7°C or ±0.50% of measured temperature | ±1.0°C or ±0.40% of measured temperature | |
| J | Above 0°C; below 750°C | ±2.2°C or ±0.75% of measured temperature | ±1.1°C or ±0.40% of measured temperature |
| T | -200°C or above; less than 0°C | ±1.0°C or ±1.50% of measured temperature | - |
| Above 0°C; below 350°C | ±1.0°C or ±0.75% of measured temperature | ±0.5°C or ±0.40% of measured temperature | |
2.JIS C1602-1995 IEC 584-2-1982 (Amendment 1-1989) BS/EN 60584-2-1993 DIN/IEC 584-2-1992
| Type | Allowable error | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | |
| B | - - |
- - |
Above 600C; below 800°C ±4°C |
| - - |
Above 600°C; below 1700°C ±0.25%·∣t∣ |
Above 800°C; below 1700°C ±.5%·∣t∣ |
|
| R·S | Above 0°C; below 1100°C ±1°C |
Above 0°C; below 600°C ±1.5°C |
- - |
| Above 1100°C; below 1600°C ±[1+0.3%·(t-1100)]°C |
Above 600°C; below 1600°C ±0.25%·∣t∣ |
- - |
|
| N | -40°C or above; less than 375°C ±1.5°C |
-40°C or above; less than 333°C ±2.5°C |
-167°C or above; less than 40°C ±2.5°C |
| Above 375°C; below 1000°C ±0.4%·∣t∣ |
Above 333°C; below 1200°C ±0.75%·∣t∣ |
-200°C or above; less than -167°C ±1.5%·∣t∣ |
|
| K | -40°C or above; less than 375°C ±1.5°C |
-40°C or above; less than 333°C ±2.5°C |
-167°C or above; less than 40°C ±2.5°C |
| Above 375°C; below 1000°C ±0.4%·∣t∣ |
Above 333°C; below 1200°C ±0.75%·∣t∣ |
-200°C or above; less than -167°C ±1.5%·∣t∣ |
|
| E | -40°C or above; less than 375°C ±1.5°C |
-40°C or above; less than 333°C ±2.5°C |
-167°C or above; less than 40°C ±2.5°C |
| Above 375°C; below 800°C ±0.4%·∣t∣ |
Above 333°C; below 900°C ±0.75%·∣t∣ |
-200°C or above; less than -167°C ±1.5%·∣t∣ |
|
| J | -40°C or above; less than 375°C ±1.5°C |
-40°C or above; less than 333°C ±2.5°C |
- - |
| Above 375°C; below 750°C ±0.4%·∣t∣ |
Above 333°C; below 750°C ±0.75%·∣t∣ |
- - |
|
| T | -40°C or above; less than 125°C ±0.5°C |
-40°C or above; less than 133°C ±1°C |
-67°C or above; less than 40°C ±1°C |
| Above 125°C; below 350°C ±0.4%·∣t∣ |
Above 133°C; below 350°C ±0.75%·∣t∣ |
-200°C or above; less than -67°C ±1.5%·∣t∣ |
|
*The commonly used specifications are listed. If you need other specifications, please call us. Please contact us.


 Technical documents
Technical documents FAQ
FAQ