Compensation wire introduction
The compensation wire is used to connect the cold junction of the thermocouple and the meter. It is divided into two types: plain wire level and compensation level. The plain wire level has higher precision but is relatively expensive. In order to reduce costs and provide a certain accuracy, you can also choose compensation level wires with similar properties.
Compensation wire insulation material and characteristics reference
(Please refer to the specifications of each model for details)
| Kinds | Applicable temperature | Non-flammable | Wear resistance | Organic solvent | Acid resistance | Moisture resistance | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic (PVC) | -20°C~105°C | Difference | Good | Difference | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Teflon(FEP) | -200°C~200°C | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Teflon (PFA) | -267°C~260°C | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| KAPTON | -267°C~316°C | Good | Excellent | Good | Good | Good | Good |
| Fiberglass (Japanese standard) | Room temperature~270°C | Excellent | Possible | Excellent | Excellent | Difference | Possible |
| Fiberglass (US regulations) | -73°C~482°C | Excellent | Possible | Excellent | Excellent | Difference | Possible |
| High temperature resistant ceramic fiber | -17°C~1200°C | Excellent | Difference | Excellent | Possible | Difference | Possible |
American wire gauge (AWG) size comparison table
| Gage No. | Wire diameter (mm) |
Cross-sectional area(mm2) | Gage No. | Wire diameter (mm) |
Cross-sectional area(mm2) | Gage No. | Wire diameter (mm) |
Cross-sectional area(mm2) | Gage No. | Wire diameter (mm) |
Cross-sectional area(mm2) | Gage No. | Wire diameter (mm) |
Cross-sectional area(mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.348 | 42.4 | 9 | 2.906 | 6.63 | 17 | 1.150 | 1.04 | 25 | 0.455 | 0.162 | 33 | 0.180 | 0.0254 |
| 2 | 6.544 | 33.6 | 10 | 2.588 | 5.26 | 18 | 1.024 | 0.823 | 26 | 0.405 | 0.129 | 34 | 0.160 | 0.0201 |
| 3 | 5.827 | 26.7 | 11 | 2.305 | 4.17 | 19 | 0.912 | 0.653 | 27 | 0.261 | 0.102 | 35 | 0.143 | 0.0160 |
| 4 | 5.189 | 21.2 | 12 | 2.053 | 3.31 | 20 | 0.812 | 0.518 | 28 | 0.321 | 0.0810 | 36 | 0.127 | 0.0127 |
| 5 | 4.621 | 16.8 | 13 | 1.828 | 2.62 | 21 | 0.723 | 0.410 | 29 | 0.286 | 0.0642 | 37 | 0.113 | 0.0100 |
| 6 | 4.115 | 13.3 | 14 | 1.628 | 2.08 | 22 | 0.644 | 0.326 | 30 | 0.255 | 0.0509 | 38 | 0.101 | 0.00797 |
| 7 | 3.665 | 10.5 | 15 | 1.450 | 1.65 | 23 | 0.573 | 0.258 | 31 | 0.227 | 0.0404 | 39 | 0.0897 | 0.00632 |
| 8 | 3.264 | 8.37 | 16 | 1.291 | 1.31 | 24 | 0.511 | 0.205 | 32 | 0.202 | 0.0320 | 40 | 0.0799 | 0.00501 |
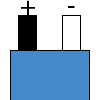
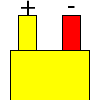
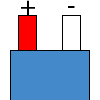
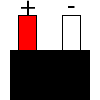
Color specifications for compensation wires and connecting plugs
| ANSI plug | ANSI/ ASTM E-230 prime line grade | ANSI/ASTM E-230 compensation grade | JIS C 1610-1989 | IEC 584-3 line level | IEC 584-3 compensation level | IEC 584-3 plug |
| J | 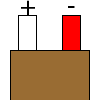 |
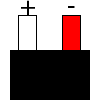 |
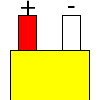 |
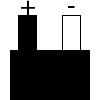 |
 |
J |
| K | 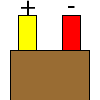 |
 |
 |
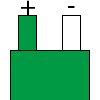 |
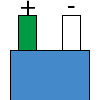 |
K |
| T | 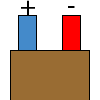 |
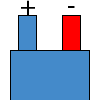 |
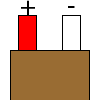 |
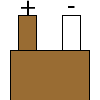 |
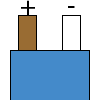 |
T |
| E | 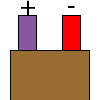 |
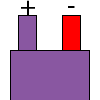 |
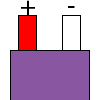 |
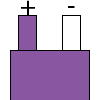 |
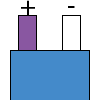 |
E |
| N | 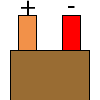 |
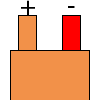 |
no specification | 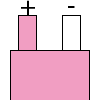 |
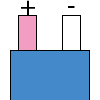 |
N |
| R | no specification | 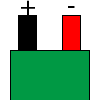 |
 |
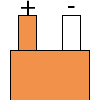 |
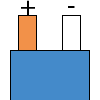 |
R |
| S | no specification |  |
 |
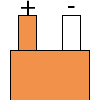 |
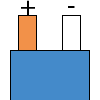 |
S |
| B | no specification | 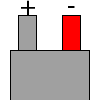 |
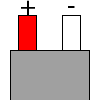 |
 |
 |
B |


 Technical documents
Technical documents FAQ
FAQ










